
Optical Imaging Unit
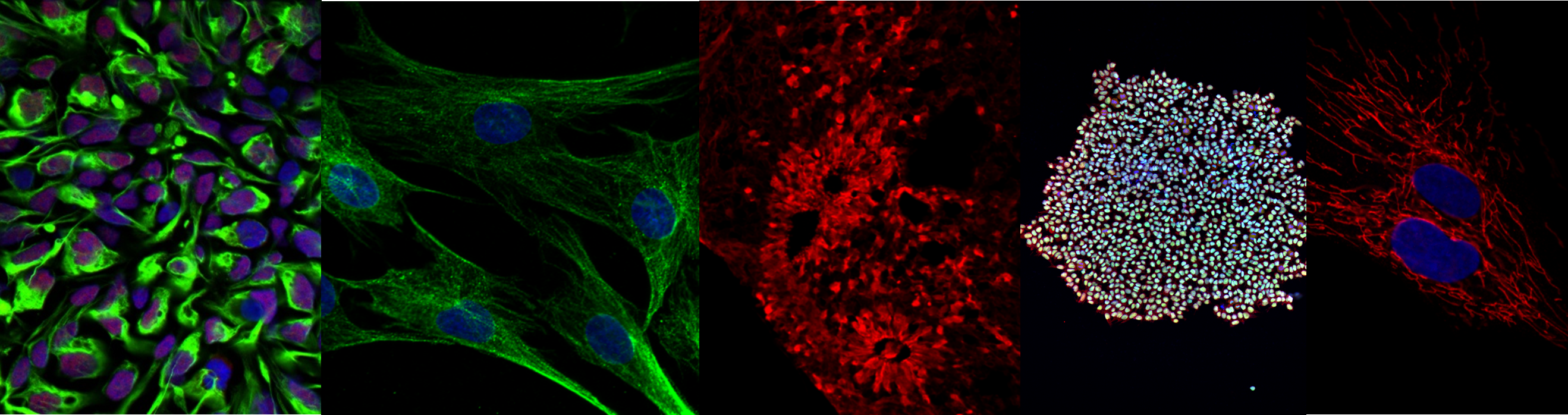
Optical imaging plays a pivotal role in a wide range of basic and translational research areas, including monitoring intracellular dynamics, analyzing protein–protein interactions, evaluating cell migration and differentiation, assessing morphological alterations, and tracking cellular signal transduction pathways. With its state-of-the-art microscopy infrastructure and highly experienced technical staff, the Unit provides qualified and sustainable support to scientific projects spanning from fundamental research to preclinical studies.
The Optical Imaging Unit is capable of high-resolution imaging of a broad spectrum of biological specimens, ranging from live cells to tissue sections. Its advanced technological infrastructure enables researchers to directly and dynamically visualize biological processes, serving both internal and external users. Comprehensive consultancy and technical support are provided throughout all stages of the optical imaging workflow, including experimental design, sample preparation, determination of optimal imaging parameters, and advanced image analysis.
Instrumentation
- Zeiss LSM880 - Laser Scanning Confocal Microscope
- Zeiss Observer 7 - Apotome Fluorescence Microscope
- Olympus BX61 - Fully Motorized Fluorescence Microscope System
- Olympus IX71 - Fluorescence Microscope
- Olympus CKX41 - Light Microscope
- Olympus IX81 - Live Cell Imaging Microscope
With this instrumentation, the following advanced imaging techniques can be performed;
- Multichannel fluorescence imaging
- 2D and 3D (Z-stack) imaging
- Whole-area imaging (Tile Scan)
- Time-series imaging (conversion of images acquired from selected locations at defined time intervals into video format)
- Super-resolution imaging (Airyscan)
In addition, the Zeiss LSM880 confocal microscope enables Correlative Light and Electron Microscopy (CLEM) analyses integrated with scanning electron microscopy (SEM).
Related Publications
1- Saglam-Metiner, P., Devamoglu, U., Filiz, Y. et al. Spatio-temporal dynamics enhance cellular diversity, neuronal function and further maturation of human cerebral organoids. Commun Biol 6, 173 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1038/s42003-023-04547-1
2- Merve Basol, Esra Ersoz-Gulseven, Helin Ozaktas, Sibel Kalyoncu, Canan Asli Utine, Gulcin Cakan-AkdoganLoss of carbohydrate sulfotransferase 6 function leads to macular corneal dystrophy phenotypes and skeletal defects in zebrafish
3- Argitekin, E., Ersoz-Gulseven, E., Cakan-Akdogan, G., & Akdogan, Y. (2023). Dopamine-conjugated bovine serum albumin nanoparticles containing pH-responsive catechol-V (III) coordination for in vitro and in vivo drug delivery. Biomacromolecules, 24(8), 3603-3618.
4- Yasar Akdogan, Sumeyra Cigdem Sozer, Cansu Akyol, Merve Basol, Cigdem Karakoyun, Gulcin Cakan-Akdogan Probing the molecular mechanism of interaction between polystyrene nanoplastics and catalase by multispectroscopic techniques 2023, Chemico Biological Interactions
5- Arslan M, Karadag M, Onal E, Gelinci E, Cakan-Akdogan G, Kalyoncu S. Effect of non-repetitive linker on in vitro and in vivo properties of an anti-VEGF scFv. Sci Rep. 2022 Mar 31;12(1):5449. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-09324-4. PMID: 35361822; PMCID: PMC8971466.
6- Burak Kahveci, Elifsu Polatli, Yalin Bastanlar, and Sinan Guven ACS Omega 2024 9 (46), 46117-46128 DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.4c06450 OrganoLabeler: A Quick and Accurate Annotation Tool for Organoid Images
7- Koc, A.C., Sari, V., Kocak, G. et al. Patient-derived cornea organoid model to study metabolomic characterization of rare disease: aniridia-associated keratopathy. BMC Ophthalmol 25, 14 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12886-024-03831-w
8- Asal M, Koçak G, Sarı V, Reçber T, Nemutlu E, Utine CA, Güven S. Development of lacrimal gland organoids from iPSC derived multizonal ocular cells. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023 Jan 4;10:1058846. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.1058846. PMID: 36684423; PMCID: PMC9846036.
9- Kurden-Pekmezci A, Cakiroglu E, Eris S, Mazi FA, Coskun-Deniz OS, Dalgic E, Oz O,Senturk S. MALT1 paracaspase is overexpressed in hepatocellular carcinoma andpromotes cancer cell survival and growth. Life Sciences. 2023 Jun 15;323:121690.
10- Mazi FA, Cakiroglu E, Uysal M, Kalyoncu M, Demirci D, Sozeri PY, Yilmaz GO, Ozhan SE, Senturk S. The paracaspase MALT1 is a downstream target of Smad3 and potentiates the crosstalk between TGF-β and NF-kB signaling pathways in cancer cells. Cellular Signalling. 2023 May 1;105:110611. DOI: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2023.110611
11- Dayanc B, Eris S, Gulfirat NE, Ozden-Yilmaz G, Cakiroglu E, Coskun Deniz OS, Karakülah G, Erkek-Ozhan S, Senturk S. Integrative multi-omics identifies AP-1 transcription factor as a targetable mediator of acquired osimertinib resistance in non-small cell lung cancer. Cell Death & Disease. 2025 May 25;16(1):414.doi: 10.1038/s41419-025-07711-z
12- Kalyoncu M, Demirci D, Eris S, Dayanc B, Cakiroglu E, Basol M, Uysal M, Cakan‐Akdogan G, Liu F, Ozturk M, Karakülah G. Escape from TGF‐β‐induced senescence promotes aggressive hallmarks in epithelial hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Molecular Oncology. 2025 Mar 14. DOI: 10.1002/1878-0261.70021
Unit Coordinator: Aslı Seren
